Faraday's law
Fondamental :
The Maxwell-Faraday equation is :
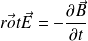
Stoke's theorem applied to a thread-like closed circuit (C) :
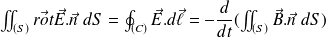
Hence :

Where :

is the magnetic flux through the circuit (C).
Attention : Faraday's law
In the Galilean laboratory, the induced electromotive force along a closed still circuit is opposed to the time derivative of the magnetic flux through the circuit :

Exemple : A video about Faraday's law of induction (CHM nano education)
Simulation : JAVA animation of Jean-Jacques Rousseau (Université du Mans)
Faraday's law : click HERE
Simulation : An animation about Faraday's law of induction (University of Colorado)
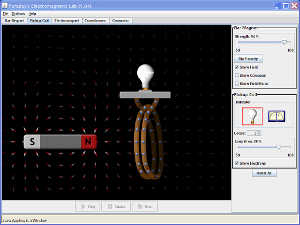
To learn Faraday's law of induction, play with magnetized bars and coils.
Move the magnetized bar close to one or two coils to turn on a light bulb.
See the magnetic field lines.
A counter measures the orientation and amplitude of the current.
See the magnetic field lines or use the counter to see the orientation and amplitude of the current.
You can also play with electromagnet, generators and transformers !
Simulation : Another animation on Faraday's law (University of Colorado)
Light up a light bulb by moving a magnet.
This demonstration of Faraday's law of induction shows how to reduce your electricity bill at the expense of your grocery bill.